Building a Networking Virtual Lab part 1: Install KVM/Libvirt on CentOS 7
Introduction
I have split this guide into three parts. Part one deals with installing KVM/Libvirt.
Part two installs VNC to connect to your remote host to use Virtual Machine Manager (VMM), Useful if you are accessing the hypervisor via a Windows or Mac computer, Linux has an installable version of VMM, making this step optional or you can manage KVM/libvirt using the CLI tool virsh. Part three deals with installing Vagrant, again this is an optional step as you can just spin up virtual devices and connect them together.
Vagrant is used to spin up a virtual environment using KVM in this instance as a Hypervisor. it can be very useful as you can build a lab that is the same as your prod network or a reproducible lab used for your studies that can easily be destroyed and rebuilt in minutes.
This guide is based on a clean install of CentOS 7.5.
Your machine must have a processor that can support the environment.
Step 1 KVM/Libvirt CentOS packages to install
Update all packages.
yum update -y
Install KVM/Libvirt packages.
yum install -y qemu-kvm qemu-img libvirt virt-install libvirt-python libguestfs libguestfs-tools virt-manager
Start KVM/Libvirt and set to start on boot.
systemctl enable libvirtd && systemctl start libvirtd
Check status of libvirtd - should show as active (running).
systemctl status libvirtd
Step 2 Create a bridge interface
A bridge interface is required for allowing VMs to access the network that the hypervisor is connected to.
Find your machines physical by running the command ip add.
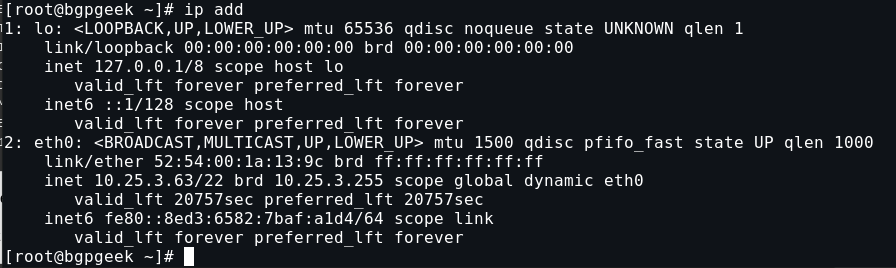
Create your bridge interface file.
cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/
vi ifcfg-br0
TYPE=Bridge
ONBOOT=yes
DEVICE=br0
BOOTPROTO=static
IPADDR=10.25.3.63
PREFIX=22
GATEWAY=10.25.0.1
DNS1=8.8.8.8
Add physical interface to bridge.
vi ifcfg-eth0
BRIDGE=br0
Restart the network service .
systemctl restart network
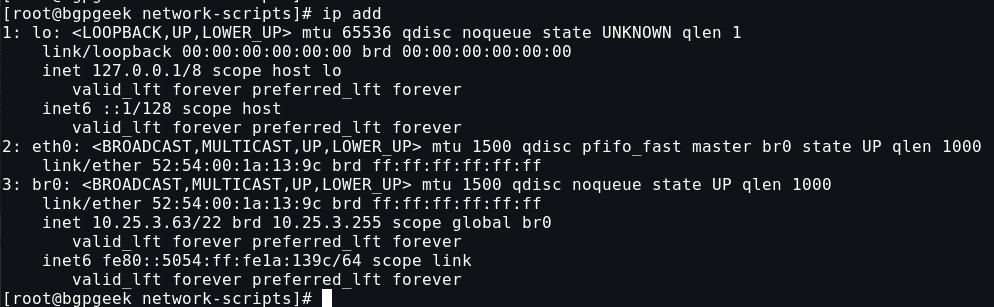
Verify br0 has the static IP address you have set.
ip add
Step 3 Optional useful utilities
Some useful packages to install.
yum install wget net-tools nano ntp
systemctl enable ntpd && systemctl start ntpd